Spatial computing is revolutionizing the way we interact with our environment, our work, and our play, and companies like Lumus are at the forefront of this digital transformation. With the AR/VR B2C industry projected to reach $31.12 billion by 2023, and experts predicting a staggering rise to $52.05 billion by 2027, there is no denying that spatial computing is a key player in the future of technology.
Spatial computing covers a broad spectrum from the real world to computer-generated reality, with augmented reality (AR), mixed reality (MR), and virtual reality (VR) being the primary technologies in use. The key differentiators among them are the levels of interaction and overlap between physical and digital elements.
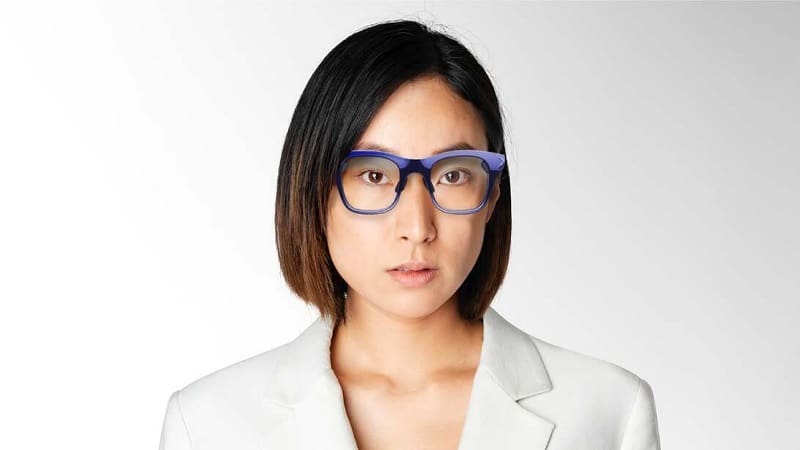
In AR, technology like XREAL air adds contextual digital information to our view of the world without interaction between physical and digital elements. This is achieved using near-to-eye display technology, allowing users to interface in 3D. Examples of AR applications include Augmedics, which superimposes anatomically correct spinal placement on patients to improve surgical outcomes, and Elbit’s Everysight, which offers designer AR glasses for IOS and Android devices. Lumus’ Z-Lens, on the other hand, combines AR functionality with vision prescriptions, eliminating the need for inserts. The AR/MR smart glasses feature a slim design, weigh less, and have no straps, offering a more natural look.
Mixed Reality adds digital elements to reality with interactive components, allowing physical and digital elements to interact. Apple Vision Pro blends digital content with physical space, while Meta Quest 3 provides an affordable option to blend digital apps and screens into the real world. As spatial computing grows, the tech is becoming smaller, with products like AR/MR smart glasses with OE Z-Lens and Apple Vision Pro shrinking in size while offering mixed reality capabilities, infrared cameras, eye tracking, and gesture recognition.
Virtual Reality offers a fully immersive digital environment with interactive components, eliminating any physical elements. Meta Quest 2 provides full virtual reality with side and top straps for stability and a 90-degree field of vision. VRpilot assists pilots in training by assessing their skills before they fly a real-life plane.
Spatial computing impacts work, play, and education in a multitude of ways. Consumers show increasing demand for AR in gaming (49%), workouts (33%), shopping (28%), real-time GPS (23%), and education (21%). In the workplace, spatial computing enables holographic business calls from any location, holographic conversations, streamlined project development, and the ability to type, text, and collaborate in documents without displays or keyboards, making work fully remote. BAE factory workers use AR to build power cells from scratch, reducing manual building time by 40%.
In the realm of play, spatial computing enhances our experiences with 3D visuals, sounds, and haptics. Games available in the metaverse, like Espire 2, The Infinite Inside, Broken Edge, PianoVision, and Niantic games like Pokémon GO, offer immersive experiences. Augmented fashion pieces, like Marga Weiman’s Hyperfabric Dress, use 3D tracking and occlusion effects for augmented additions. Spatial sound in consumer-grade AR glasses directs noise through tiny bones near the ear, reducing tinnitus or hearing loss risks. AR-enhanced karaoke allows users to see song lyrics in their glasses as a personal teleprompter.
In education, spatial computing enhances interactive learning, allowing teachers to present rich interactive media, create haptic learning experiences, and enable students to display shareable presentations. Interactive trips let learners visit locations, landmarks, and even historical time periods. Spatial computing also facilitates writing interaction notes, allowing students to write notes anytime and access them from anywhere.
Spatial computing benefits the health sector by gathering biometric data, personalizing patient care, and making staff improvements. AR-assisted procedures, simpler hospital navigation, and access to real-time patient records enhance healthcare provision.
As near-to-eye displays become more common, smartphones are losing relevance for tasks outside phone calls. In 2023, the global smartphone market declined by 14%, while global AR glasses sales rose by over 45%. Waveguide technology, especially reflective waveguides, is the heart and soul of AR glasses. Reflective waveguides expand the pupil, project images toward the eye, provide five to ten times greater battery efficiency, and up to ten times higher brightness.
With new developments on the horizon, spatial computing is poised to completely transform how humans interact both online and offline. Lumus and other innovators are ushering in a future where spatial computing is not just a tech trend but an integral part of our daily lives.